The Complete Guide To The Keto Diet
Table Of Contents
HISTORY OF THE KETOGENIC DIET.
HOW TO START THE KETOGENIC DIET.
WATCH THE VIDEO LINK HERE FOR A COMPLETE EXPLANATION OF THESE POINTS:
WHAT CAN I EAT ON THE KETOGENIC DIET?.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF FAT THAT I CAN EAT?.
SATURATED FATS (EAT MEAT, DAIRY)
MONOUNSATURATED FAT (EAT AVOCADOS, OLIVE OIL, CASHEWS)
DO I HAVE TO EAT COCONUT OIL / MCT OIL?.
HOW MANY CARBOHYDRATES CAN YOU EAT ON THE KETOGENIC DIET?.
LAZY KETO IS SIMPLY LIMITING THE NUMBER OF CARBOHYDRATES YOU EAT.
WON’T I BECOME TIRED IF I CUT OUT THE CARBS?.
CHOLESTEROL AND THE KETO DIET.
EATING A HIGH CHOLESTEROL DIET DOES NOT INCREASE HEART DISEASE
KETO DIET RISKS – HOW YOU CAN AVOID THEM
I’M NOT LOSING WEIGHT. WHAT AM I DOING WRONG?
BUT THE LABEL SAYS SUGAR-FREE!
I LIKE “INSERT FAVOURITE JUNK FOOD”. CAN I EAT LOW CARB REPLACEMENTS?
Introduction
You might not believe that weight loss without exercise is possible. You probably don’t believe it’s possible to improve your current exercise performance levels. You think it’s impossible to build muscle whilst restricting carbohydrates, and most of all, you don’t believe increasing your fat intake could ever be healthy.
You’ve probably heard about the ketogenic diet, but if you haven’t, I’m going to explain it in very simple terms.
The basic idea of the ketogenic diet is focused on enabling your own body to turn to fat for energy instead of carbohydrates, or protein.
There are many benefits to eating a Ketogenic Diet.
The main concept of ketogenic weight loss is to help you be in a state of caloric restriction without maintaining the sufficient calories and being hungry. Your body just burns its own fat as it needs to.
Excess carbohydrates turn to fat in the body anyway, so doesn’t it make sense to train your body to burn fat if you want to lose fat?
WHY SHOULD YOU GO KETO?
So why would we want to reduce the amount of sugar we consume and switch our bodies over to burn fat instead?
- Metabolically, fat is a superior fuel for the body
- Consuming fats enhances your brain function and gives mental stability
- Greater health and longevity that comes from controlling your blood sugar levels naturally.
Ketones (produced by burning fat) are the preferred fuel source for vital organs such as the muscles, heart, liver, and brain. Let’s look at some of the other benefits to nutritional ketosis:
- Natural hunger control
- Lowered inflammation levels
- Normalised metabolic function
- Lowered blood pressure
- Mental clarity
- Effortless weight loss
- Reduced triglycerides
- Lowered levels of LDL particles (bad cholesterol)
- Increased levels of HDL particles (good cholesterol)
- Increased sex drive
- Better fertility
- Eliminated heartburn
- Improved immune system
- Slowing the aging process
- Reduced acne breakouts
- Faster recovery from exercise
- Decreased anxiety and mood swings
- ……we could go on and on!
Not only does nutritional ketosis benefit the body, weight issues also respond extremely well to the approach.
A study by Harvard School of Public Health analysed 53 studies involving 67,000 dieters and found that those who cut back on carbs were two and a half pounds lighter after a year than those who embraced a “low fat” approach.
For decades, there has been debate over the merits of a low-fat diet, which was endorsed as the best route to weight loss in the 1970s. Now, major research published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, back a low carbohydrate approach as a more effective diet.
HISTORY OF THE KETOGENIC DIET
One of the most misunderstood concepts in history is this one – fat makes you fat. Does this logic apply to, for instance, going green after eating too many cucumbers? Of course not! Fat will make you fat only when it is paired with excess carbohydrates.
All the studies that say fat causes heart disease link back to one study, and it’s the reason why we think saturated fat causes heart disease. It was developed in the early 1950s by Ancel Benjamin Keys.
In his lab, Keys ran experiments looking for early indications of disease. What you must remember is that in the 1950’s, no health issue seemed more urgent than heart disease.
Keys’ most famous findings were contained in the Seven Countries Study, which showed that the risk and rates of heart attack and stroke cardiovascular risk, both at the population level and the individual level, were directly correlated to the level of total serum cholesterol.
It demonstrated that the association between blood cholesterol level and coronary heart disease (CHD) risk from 5 to 40 years’ follow-up is found consistently across different cultures.
Even before the study had begun, its methods had been criticised. Jacob Yerushalmy and Herman E. Hilleboe pointed out that, for an earlier study demonstrating this association, Keys had selected six countries out of 21 for which data were available.
Analysis of the full dataset made the analysis of fat intake and heart disease unclear. Because of this, the association between the percentage of fat calories and mortality from heart disease was not valid.
It wasn’t until 2014 when Nina Teicholz (author of “The Big Fat Surprise”) reviewed the study, and in doing so found that one country, Crete, whose results formed the majority of the evidence from the study, was conducted during Lent, thereby causing Keys to dramatically undercount the amount of saturated fat eaten.
CORRELATION VS CAUSATION
Correlation is very different from causation. You cannot draw conclusions like Keys did based on correlation. Following are some examples of illogically inferring causation from correlation:
EXAMPLE 1
THE FASTER WINDMILLS ARE OBSERVED TO ROTATE; THE MORE WIND THERE IS OBSERVED TO BE.
THEREFORE, WIND IS CAUSED BY THE ROTATION OF WINDMILLS.
(OR, SIMPLY PUT: WINDMILLS, AS THEIR NAME INDICATES, ARE MACHINES USED TO PRODUCE WIND.)
EXAMPLE 2
AS ICE CREAM SALES INCREASE, THE RATE OF DROWNING DEATHS INCREASES SHARPLY.
THEREFORE, ICE CREAM CONSUMPTION CAUSES DROWNING.
EXAMPLE 3
SINCE THE 1950S, BOTH THE ATMOSPHERIC CO2 LEVEL AND OBESITY LEVELS HAVE INCREASED SHARPLY.
HENCE, ATMOSPHERIC CO2 CAUSES OBESITY.
HOW TO START THE KETOGENIC DIET
“What advice would you give to a beginner?”
As a beginner, it’s helpful to gain information from other people who have already started the ketogenic diet. Whilst I’m here to guide you, I’ve also solicited the help of others by putting together the various advice I’ve received throughout my own journey.
I’ve compiled these responses into a list, then ordered the topics by popularity. The result is the best advice from people just like you, who have already started the ketogenic diet:
- Simplicity – Keep it simple!
- Electrolytes – salt, magnesium and potassium
- Nutrition – real food doesn’t have ingredients, it is ingredients
- Persistence – just get through that first week
- Science – have a brief understanding on how the ketogenic diet works.
WATCH THE VIDEO LINK HERE FOR A COMPLETE EXPLANATION OF THESE POINTS:
By now, you should have a simple grasp on how to start the ketogenic diet, but for a more in-depth explanation on how to start the ketogenic diet the right way the first time, read on!
WHAT CAN I EAT ON THE KETOGENIC DIET?
Ketogenic diets can be different for everyone. Eat dark green leafy vegetables, fatty red meats, chicken with the skin left on, fish, offal (organ meat), eggs, seeds & nuts, full-fat dairy, or anything else rich in nutrition, fat, protein and fibre.
Carbs are a limit. Protein is a target. Fat is to be consumed to remove hunger and meet macros requirements.
FATS & OILS
Try to get your fat from natural sources like meat and nuts. Supplement with saturated and monounsaturated fats like coconut oil, butter, and olive oil.
PROTEIN
Try to stick with organic, pasture-raised and grass-fed meat where possible. Most meats don’t have added sugar in them, so they can be consumed in moderate quantity. Remember that too much protein on a ketogenic diet is not a good thing.
VEGETABLES
Fresh is preferred, but frozen works too. Stick with above ground vegetables, leaning toward leafy/green options.
DAIRY
Most dairy is fine apart from milk. Make sure to buy full-fat dairy items. Harder cheeses typically have fewer carbs.
NUTS & SEEDS
In moderation, nuts and seeds can be used to create some fantastic textures. Try to use fattier nuts like macadamias and almonds.
BEVERAGES
Stay simple and stick to mostly water. You can flavour it if needed with stevia-based flavourings or lemon/lime juice.
MACRONUTRIENTS EXPLAINED
The main building blocks of food are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These are called macro nutrients. Just remember, macro means big, and micro means small.
Every piece of food is made up of a ratio of these building blocks.
For example, chicken breast is high in protein, and pasta is high in carbohydrates.
Currently, most people eat a standard diet containing around 20% fats, 30% protein and 50% carbohydrates. It can be hard to venture outside of these well-known macro ratios.
The ketogenic diet simply changes the ratio of these macronutrients. By limiting carbohydrates, moderating protein and increasing your total healthy fat intake, you put your body into a state of “ketosis.” Instead of burning sugar and glucose for energy, your body starts to burn “ketones,” which is an energy source that your body creates from fat.
Your body prefers burning fat for energy and it is the preferred source in your brain and muscles. It also has some remarkably positive results for many common chronic illnesses today.
Unfortunately, the general public haven’t necessarily been exposed to the truth about nutritional ketosis, and therefore don’t believe that it’s a healthy state to be in.
Just as cholesterol was falsely labelled as a culprit for heart disease, ketones have been labelled as some kind of strange substance that you should avoid at all costs. This is simply not the case.
Your body will become what is called “fat adapted” whilst you re-teach it to use the stored fat as energy, all without feeling any starvation or typical diet hunger issues.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF FAT THAT I CAN EAT?
Recommended fats to eat are olive oil, grass-fed butter, and coconut oil.
There are actually four main types of fats. These are:
TRANS FATS
The most important fat to AVOID is Trans Fats. These types of fats have been chemically altered and industrially produced to improve their physical appearance and taste. This method, however, has been shown to significantly increase LDL cholesterol in humans (the bad one) by about 10% and has no impact on the protective HDL cholesterol.
Trans fat is a variant of unsaturated fat. 50 years ago, saturated fats were thought to be the enemy, as they were incorrectly linked with certain diseases. When trans fats were first introduced to food production, they were considered miraculous because they allowed a liquid oil to be converted to a solid spread without the “adverse effects” of saturated fat on blood cholesterol.
By 1990, research by Mensink and Katan showed trans fats elevated the harmful LDL cholesterol by about a tenth more than regular unsaturated fat. Compared with other fats, trans fats didn’t have the benefit of elevating the protective HDL cholesterol. Mensink and Katan concluded that trans fats were the worst type of food that contributed to heart disease.
This was shown convincingly by Walter Willett in his 1993 study of US nurses. Those who reported eating a large number of trans fats (more than 5.7 grams a day) were around two-thirds more likely to have a heart attack than nurses eating less than 2.4 grams a day.
Trans fats from dairy and beef fat (“natural” trans) were not linked to heart disease risk.
SATURATED FATS (EAT MEAT, DAIRY)
Saturated fats are usually a solid at room temperature and oxidize slowly. They have a stable composition, which is why they are solid. This type of fat is most often found in animal foods including:
- Meat
- Dairy products.
MONOUNSATURATED FAT (EAT AVOCADOS, OLIVE OIL, CASHEWS)
Monounsaturated fats are usually a liquid at room temperature. They have a weak composition which is why they convert to liquid easily. Monounsaturated fats are most often found in:
- Avocados
- Olives
- Almonds and cashews
- Olive oil and sesame oil.
POLYUNSATURATED FAT (Sunflower Oil, Corn Oil, Soybean Oil, Omega 3, Omega 6)
Polyunsaturated fats can be tricky. This type of fat is mostly found in the following foods:
- Sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds
- Corn oil, safflower oil, and soybean oil
- Pine nuts and walnuts.
There is also a specific type of polyunsaturated fat called Omega 3 Fats, studied due to their significant effect on heart health and ability to lower triglyceride levels and increase high-density lipoproteins. This type of fat is best balanced with omega 6 fats at a ratio of 1:1, but you won’t have to worry about that as long as you are eating whole foods. These particular fats can be found in the following:
- Fatty fish – including salmon, mackerel, herring, and tuna
- Certain seeds – including flax seeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
DO I HAVE TO EAT COCONUT OIL / MCT OIL?
Medium Chain Triglyceride (MCT) is a special type of saturated fat converted straight into energy by your liver and cannot be stored as fat.
The energy boosts you get from MCT oil is similar to carbs and is important to help you switch over to fat burning as easily as possible.
Coconut contains just over 60% MCT, so it’s a beneficial way to get energy from a high-fat diet. MCT oil in particular has made a huge difference for me, especially when I tried the high-intensity cardio exercise on a keto diet, but mostly to keep my energy levels at an optimum level.
According to Dr. Laurie Cullen at the Women’s Institute, when MCTs are absorbed into the bloodstream, they bypass the digestion process that longer chain fats go through.
MCT’s provide quick energy for the body and are thus less likely to be stored in the fat cells. Further, Dr. Cullen says when a meal includes medium chain triglycerides, there is a significant increase in the amount of calories burned (thermogenic effect). When more calories are used, fewer are stored as fat, which helps reduce body fat levels.
Many keto diets and MCT oil spokespeople say MCT’s energy sustaining powers can be explained as follows: when MCT oil is metabolized in the body, it behaves more like a carbohydrate energy source than a fat.
Remember, your current fuel preference for the body is carbohydrate (until you become fat adapted). Unlike other fats, MCT oil does not go through the lymphatic system. Instead, it is transported directly to the liver where it is metabolized so it releases energy like a carbohydrate and creates significant ketones (which can be used for fuel) in the process.
HOW MANY CARBOHYDRATES CAN YOU EAT ON THE KETOGENIC DIET?
Strictly speaking, the simple rule that most people follow is under 20 carbohydrates per day. What does that look like?
Your body will always attempt to use carbohydrates as a source of energy because they are so easily broken down into sugar in your body. This doesn’t mean, however, that your body runs well on this fuel.
If you pull into a gas station, there is always a couple of different types of fuel you can choose to fill up with.
Carbohydrates are like the cheapest, dirtiest fuel, whilst fats are similar to the premium fuel. The cheap fuel will still get you to your destination, but it’s filling your car with issues that you will have to pay for in the future.
Your body prefers running on healthy fats because they cause less inflammation, are longer lasting, and you can store the fuel easily on your body. Carbohydrates have to be turned into fat to be stored and will only be used when there is a lack of carbohydrates available.
Carbohydrate Example


LAZY KETO IS SIMPLY LIMITING THE NUMBER OF CARBOHYDRATES YOU EAT.
A keto diet is just a low carb diet coupled with a higher fat intake. The amount of carbs depends on each person, but it usually below 50 grams of net carbs per day. If you eat 10 grams of carbs, but that contains 5 grams of fibre, you will have consumed 5 grams of net carbs.
This limited amount of carbohydrate intake will switch your body over to burning ketones as your primary source of fuel. Alternatively, you can look at your body switching from being a sugar burning steam train with all the dirty black soot covering the engine, to a clean burning Tesla that runs on fat and ultimately does less damage to your body.
Keto diets are low in carbohydrates. This means you should avoid the following foods:
- Bread
- Pasta
- Sugar
- Milk
- Corn
- Beans
- Rice*
- Fruit*
*Unless you are refueling from exercise – still limit these.
What most people don’t understand is that this is a normal metabolic state. When babies are born, they will go into a state of nutritional ketosis, relying on their mother’s breast milk, which provides 25% energy from ketones. If you have ever skipped breakfast, you would most certainly have been in a state of Ketosis.
WON’T I BECOME TIRED IF I CUT OUT THE CARBS?
Carbs do equal energy, but like sugar, they only last for a limited amount of time. There is a by-product of fat consumption which is called Ketones.
In a state of carbohydrate depletion, ketones are used in your body as energy, particularly in the brain. Put simply, burning fat whilst being in a low carb state, also equals energy! And much more of it.
The Keto Diet can make you feel much more alert because your brain is getting much more energy from ketones than it ever did from carbohydrates.
WHAT OTHER CONDITIONS WILL A KETO DIET HELP?
There is a great amount of science-based evidence showing that the following conditions can be reversed or greatly improved on a keto diet.
A keto diet has been used for many years to treat epilepsy. By stabilizing energy production and increasing blood ketone levels, the body is able to control seizures.
Blood ketone levels are also showing strong signs in the treatments of certain disorders such as Autism, ALS, Parkinson’s disease and MS.
We know that aging is a result of the destruction of the human body, but you might not be aware that inflammation can accelerate aging. A keto diet can reduce inflammation significantly, therefore preventing the aging process.
Endurance athletes may be surprised to know that a keto diet can help with mitochondrial support, as it increases oxygen uptake and increases the efficiency of the mitochondrial biomechanics. This, in turn, can help in diseases such as Glucose Transporter Type 1 Deficiency, McArdle’s Disease, and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Deficiency.
DIABETES AND INGESTING FAT
Type 2 Diabetes is one of the most avoidable diseases in the western world, and it has
become an epidemic. Most of our population just don’t understand what causes this disease.
People with diabetes are not affected most by large amounts of fat or protein. Insulin resistance is the key cause, and guess what causes insulin resistance; taking a ride on the carbohydrate roller coaster every 3-4 hours which eventually leads to insulin resistance, along with other factors.When a person with diabetes eats a burger and fries, it’s the carbohydrate one that sends their blood glucose spiraling out of control, not the meat and cheese. Fat is not to blame at all, it just happens to take the fall.
WHAT IS INSULIN RESISTANCE?
Before we talk about insulin resistance, let’s talk about insulin. Insulin is made by your pancreas and allows your body to use glucose (sugar) from carbohydrates in your diet.
This particular molecule helps keep your blood sugar levels from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
A good way to remember this is that HYPER comes from too much sugar, and HYPO comes from not enough.
Your body regulates the amount of blood sugar in the blood by insulin. When the body has too much excess insulin, it can become insulin resistant. This has the ability to cause a multitude of other chronic health risks, including PCOS (For women) and Fatty Liver Disease.
CHOLESTEROL AND THE KETO DIET
Cholesterol plays an important role in our survival. The liver is careful to ensure the body always has enough, creating around 1000 – 1400 milligrams of it each day. The liver also has important feedback mechanisms that regulate how much it needs to produce from how much we get from our diet.
Cholesterol’s main job is to insulate parts of our cells, build and maintain cell membranes, help digest fat soluble vitamins like Vitamin D (sun), E (skin), A (eyesight) and K (blood clotting) whilst also kick-starting many of the body’s own pathways to producing hormones, including sex hormones!
Cardiac risk factors improve when blood sugar and insulin levels are lowered via dietary changes. HDL cholesterol goes up on a low carb, high-fat diet and triglycerides fall dramatically.
EATING A HIGH CHOLESTEROL DIET DOES NOT INCREASE HEART DISEASE
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition undertook a study proving that eating a high-cholesterol diet does not increase the risk of heart disease.
The study followed 1,032 initially healthy men aged 42 to 60. The men consumed an average of about 2,800 milligrams of cholesterol a week; more than a quarter of it from eating an average of four eggs weekly. (An egg contains about 180 milligrams of cholesterol.)
After controlling for age, education, smoking, B.M.I., diabetes, hypertension, and other characteristics, the researchers found no association between cardiovascular disease and total cholesterol or egg consumption. The researchers also examined carotid artery thickness, a measure of atherosclerosis. They found no association between cholesterol consumption and artery thickness, either.
In Europe, The Countries That Eat the Most Saturated Fat Have the Lowest Risk of Heart Disease
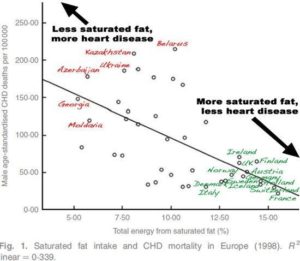
Data from: Hoenselaar R. Further response from Hoenselaar. British Journal of Nutrition, 2012.
The Obesity Epidemic in The USA Started at Almost The Exact Same Time The Low-Fat Dietary Guidelines Were Published
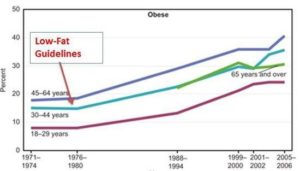
Source: National Center for Health Statistics (US). Health, United States, 2008: With Special Feature on the Health of Young Adults. Hyattsville (MD): National Center for Health Statistics (US); 2009 Mar. Chartbook.
The Diseases of Civilization Increased as Butter and Lard Were Replaced with Vegetable Oils and Trans Fats
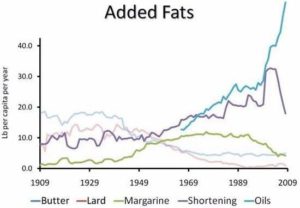
Source: Dr. Stephan Guyenet. The American Diet. 2012.
KETO DIET RISKS – HOW YOU CAN AVOID THEM
For those who are unfamiliar with the keto diet, it’s relatively simple. The keto diet is basically a low carb, high fat diet which consists of healthy fats, moderate amounts of protein and a very strict limit on carbohydrates.
What is becoming more prominent recently as the lifestyle has become more mainstream makes me frustrated.
NUTRITION
Specifically, when micronutrition gets thrown out in favour of the low carb, high fat macros.
It basically looks like this. When someone starts a ketogenic lifestyle, the hardest part is cutting out the sugar in your diet. Sometimes, people do both sugar and carbohydrates in one go. Kudos to those people! Sugar is extremely addictive, and carbohydrates have been deemed necessary for energy ever since the low-fat brigade made their way to the top.
However, what begins to happen is this. That person begins to eat an incredibly high amount of processed foods, just because the macronutrients fit the ratios required. They discard nutritious foods just because the macro nutrition of vegetables doesn’t fit the strict food rules that the keto diet implies.
It often gets to the point where instead of eating living plants, natural foods, and drinking water, they substitute everything they can with a low carb alternative that is either filled with preservatives, artificially sweetened with aspartame, or has lived in a can for the past four years.
How many carbs does a cigarette have? – Is it good for your health? NO.
Hypothetically, eating a diet solely consisting of cheese will help you lose weight. This might work for the first weight loss goal because you’ve effectively cut out all the insulin-raising foods that prevented you from losing weight in the first place. But if you want to look after your health, then you really need to learn to understand what you’re actually eating, regardless of the carbohydrate and fat content.
The biggest keto diet risks come from ignoring your body and nutrition.
So many people are deficient in many of the vital micronutrients because all they eat is salami and artificial cheese sticks. Some of these include magnesium, zinc and vitamins A, B, C and D.
You need to teach your body to re-learn what it actually needs, instead of switching from coke to diet coke, or bakery goods to an entire box of low carb sugar-free cookies. The physical food needs to change, but so does your mindset about eating food.
My aim throughout this website is to teach you which items/mindsets are important to change for lifelong success.
Don’t jump off a cliff with everyone else. Make sure you are eating healthy fats, nutritious sources of protein and a low carbohydrate content. Don’t blindly follow everything you read.
Most of all, where ever possible, make those food choices organic, ethically sourced or free from known carcinogens listed here.
I’M NOT LOSING WEIGHT. WHAT AM I DOING WRONG?
Many people decide to start a ketogenic lifestyle initially to lose weight. Remember, you’re not doing anything wrong if you are not losing weight. At first, the weight seems to slide off due to the water loss by restricting carbohydrates, however, after a while you might not be seeing the results that you loved during the start of the lifestyle.
This is because by eating less sugar and carbohydrates, you begin to increase your insulin sensitivity, which enables your body to build muscle.
To avoid disappointment, make sure you take body measurements when the number on the scales isn’t going down. Progress pictures can give a visual representation of where you are in your ketogenic journey, but it is useful to track your waist, butt, and arm measurements.
During plateaus, you will still be shedding inches, but the scale might not necessarily move as quickly. Just keep going for the sake of whom you want to become.
Just remember, Keep Calm and Keto On!
BUT THE LABEL SAYS SUGAR-FREE!
Just because the food wrapper says it is sugar-free, it does not mean it has no carbs. Or just because it is beef jerky, it does not mean it has no sugar. I’ve fallen into this trap a few times, turning around the packet to realize that its full of sugar!
Honestly, there are not that many keto friendly foods on the shelves at the supermarket. Keep to the outer edges of the supermarket and avoid the isles where all the packaged food is positioned. Every time you go, write down new foods that are keto friendly. In a couple of months, you will have a full list of foods that you can eat at your store.
I LIKE “INSERT FAVOURITE JUNK FOOD”. CAN I EAT LOW CARB REPLACEMENTS?
One of the first things I did, when switching to keto is finding replacements for my favorite junk foods. Pizza, chips, pastries, cookies, fast foods. The problem I have with low carb replacements is I would still overeat and not hit my macros.
I had to go back, change my lifestyle, and stick to veggies, meats, and healthy fats. Once I thought of it as a lifestyle change and not a diet, it became much easier for me.
To make it really easy:
- Eat a palm-sized piece of protein with every meal
- Use vegetables as fat delivery systems (think butter with broccoli)
- Limit carbs.
Once you have been in Ketosis for a while (a few months), you can enter Ketosis again very easily, generally within two days.
However, if you are just starting out, make sure you stick with it for a while to see the real benefits before falling off the bandwagon. The results will speak for themselves!
JUST ONE WON’T HURT, RIGHT?
Let’s admit it; most people have cheat days in their diet. You are not going to die if you eat a donut. For me, it becomes a slippery slope, where a cheat day becomes a cheat week.
Practice self-control. The trick that I learned is not to trust my first instinct. If you are in a cafeteria and you tell yourself that you want a donut, tell yourself that your first instinct is incorrect when it comes to food.
Some people have pictures on their phone to remind them where they were on the journey a couple of months ago to help them not cheat.
However, if you must cheat every now and again, don’t think that you’ve ruined everything, just make sure you get back on track. Meal plans and meal preparation are key processes that make your life easier as you begin a ketogenic lifestyle.
Summary
The post The Complete Guide To The Keto Diet appeared first on FatForWeightLoss.
from FatForWeightLoss https://ift.tt/2uZXQ9a



Post a Comment